Key Takeaways
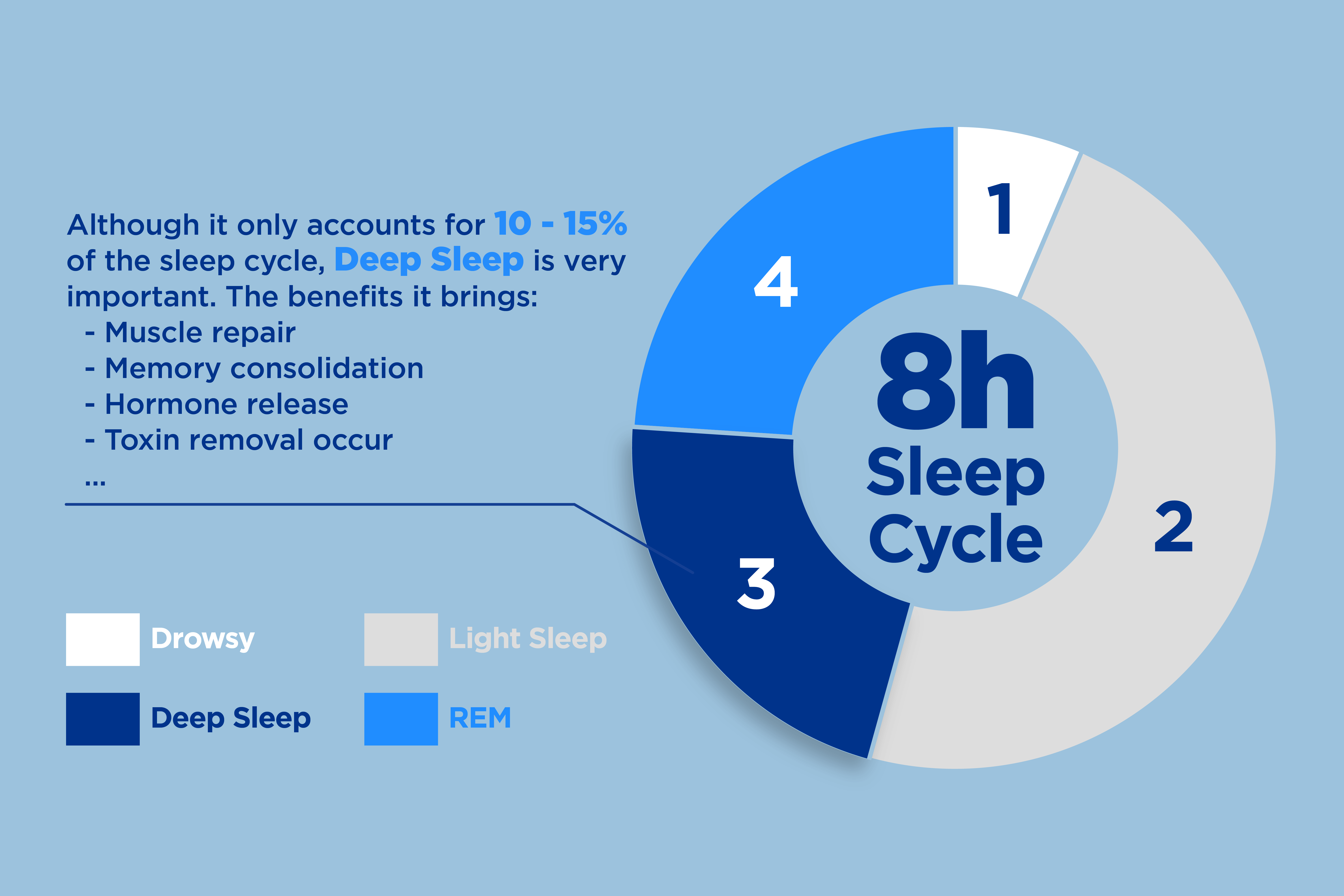
- What Is Deep Sleep: Also known as slow-wave sleep, deep sleep is a crucial stage of the sleep cycle when brain waves slow down, the body recovers, and essential processes like human growth hormone release and toxin removal occur. Adults typically need 7 to 9 hours of sleep, with 10-15% of that time spent in deep sleep.
- How to Get More Deep Sleep: Prioritizing healthy sleep habits can help you achieve better sleep quality and experience the benefits of deep sleep, including improved cognitive function and reduced health risks.
- Good Sleep Habits: Develop a consistent bedtime routine that includes relaxing activities like reading or taking a warm bath. Set a regular wake time to establish a sleep-wake pattern that enhances sleep quality. And consider investing in a new mattress and pillow for added comfort and support during sleep.
Deep sleep, also known as delta sleep or slow-wave sleep, is one type of non-REM sleep. Brain waves slow down, and the body recovers from the day’s activities—injuries heal, human growth hormone is released, and toxins are cleared from the cerebrospinal fluid. The average adult needs 7 to 9 hours of sleep and spends 10-15% of it in deep sleep.
In our article, we share 8 tips on how to get more deep sleep and fall asleep quickly with fewer disruptions.
Quick Guide: A 30-Second Summary
| Best Mattress Overall | Amerisleep AS3 |
| Best Cooling Tencel Sheets | Amerisleep Tencel Sheets |
| Best Cooling Bamboo Sheets | Amerisleep Bamboo Sheets |
Turn Off Electronic Devices
Limiting screen time at night and turning off your cell phone before bedtime gives you a chance to relax before falling asleep. Too much blue light exposure can disrupt melatonin production, a hormone that helps to regulate the circadian sleep-wake rhythm and tells the brain that it is time for sleep at night.
Many cell phones have “night” mode, so the screen gives off orange light instead of blue light. Instead of scrolling on your phone or laptop, we suggest reading a book or drawing. If you can avoid it, don’t keep a TV in the bedroom.
If you can, you might want to establish your bedroom as a tech-free zone. Doing so can help to decrease sleep disruptors at night, potentially allowing you to sleep more deeply.
Keep the Bedroom Dark and Cool and Quiet
 The bedroom should be dark and cool for quality sleep. A dark room encourages
melatonin
Verified Source
National Library of Medicine (NIH)
World’s largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible.
View source
production, a circadian hormone that tells the brain it is time to sleep at night.
The bedroom should be dark and cool for quality sleep. A dark room encourages
melatonin
Verified Source
National Library of Medicine (NIH)
World’s largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible.
View source
production, a circadian hormone that tells the brain it is time to sleep at night.
Extreme room temperature also affects sleep. A study by the NIH Verified Source National Library of Medicine (NIH) World’s largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible. View source found that, as long as you have enough bedcovers to stay warm enough for comfort, having a cold room is not detrimental to sleep. In fact, a process called thermoregulation helps the body to maintain its core temperature. However, having a room that is too hot (close to 90 degrees Fahrenheit) can decrease deep sleep.
 Even if you can’t entirely control your room temperature for better sleep, you can take simple steps such as:
Even if you can’t entirely control your room temperature for better sleep, you can take simple steps such as:
- Wearing light sleepwear in the summer
- Using breathable bedding
- Purchasing a small fan, though sleeping with a fan on has its pros and cons
- Cooling off before bed with a shower
You can also prepare for a cool night’s rest during the day, without turning on the air conditioner. Keep your bedroom dark and cool when it’s day and open windows in the evening to encourage a refreshing chill.
Also, try to prevent any sound from waking you up by wearing earplugs, since the brain still processes noise and could signal the body to wake up if there is too much disturbance in the environment.
If you need to a go a step further, consider ways you can block noise from the bedroom, such as sound-dampening panels and a thicker bedroom door.
Develop a Bedtime Routine
 Taking a hot bath or shower and reading a book every night helps your mind associate these activities with bedtime. One study found that children
slept better
Verified Source
American Academy of Sleep Medicine
Society focused on sleep medicine and disorders, and the AASM is who authorizes U.S. sleep medicine facilities.
View source
if they followed a nightly routine. These children experienced an hour more of sleep compared to children who didn’t follow a routine.
Taking a hot bath or shower and reading a book every night helps your mind associate these activities with bedtime. One study found that children
slept better
Verified Source
American Academy of Sleep Medicine
Society focused on sleep medicine and disorders, and the AASM is who authorizes U.S. sleep medicine facilities.
View source
if they followed a nightly routine. These children experienced an hour more of sleep compared to children who didn’t follow a routine.
“Adults can do this too,” explains Dr. Jade Wu, sleep psychologist, “As long as they’re not too strict with themselves, such as being rigid about doing a bedtime routine in the exact same way at the exact same time every evening). This can create performance anxiety for sleep.”
Similarly, what you cut out before bed can also contribute to your bedtime routine. We already mentioned turning off your devices, and you should try to avoid eating before bed, too.
Set a Consistent Rise Time

A wake time establishes a pattern and helps your circadian system to be regular and robust, which helps your sleep quality. Going to bed at around the same time in the evenings will become easier to do once you’ve established a regular rise time.
Try to follow the same sleep-wake schedule during the weekend. It’s tempting to sleep in, but this could break your internal clock and disrupt sleep patterns.
Choose Breathable Bedding
 Breathable bedding regulates temperature and moisture, allowing for better air circulation and preventing the buildup of heat and humidity. This feature is particularly beneficial for individuals who tend to sleep hot or sweat during the night.
Breathable bedding regulates temperature and moisture, allowing for better air circulation and preventing the buildup of heat and humidity. This feature is particularly beneficial for individuals who tend to sleep hot or sweat during the night.
Bedding and pajamas made from cotton, Tencel®, and bamboo ensures you sleep cool. These materials are more breathable than fabrics like polyester or microfiber, which are prone to trapping body heat.
Try Aromatherapy
Diffusing certain essential oils Verified Source National Library of Medicine (NIH) World’s largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible. View source may reduce stress and help you to feel more relaxed as you prepare for sleep. Essential oils, like lavender and clary sage, release tension and lower heart rate, promoting feelings of calm. Start diffusing your favorite sleep essential oil in the evening to help you wind down.
If you don’t have a diffuser, add 6 to 10 drops of your favorite sleepy time essential oil to a spray bottle, then fill the bottle with cold water. Spray into the air right before bedtime.
You can also try a few drops of essential oil in a pillow spray for sleep.
Follow a Healthy Diet
Avoid rich, heavy meals Verified Source National Library of Medicine (NIH) World’s largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible. View source right before bedtime, because eating a large meal and then lying horizontally can cause acid reflux. Instead, try some low-carbohydrate options before bed, like cottage cheese or celery with peanut butter. These foods, high in protein and complex carbs, will curb hunger pains without disrupting your sleep.
Exercise Regularly
Moderate to intense exercise at least three times a day for 30 minutes improves deep sleep by increasing your heart rate and working your muscles. Aerobic exercise Verified Source Johns Hopkins Medicine University focused on medical research that produces thoroughly reviewed health articles. View source causes the body to release endorphins, chemicals that keep you awake. Working out also increases your exposure to sunlight when exercising outside and reduces melatonin production during the day. After a workout, the body cools down and drops in temperature, endorphin levels decrease, and you feel sleepy.
The best time to exercise is in the morning or afternoon. Try to avoid exercising right before bedtime, because this may be overstimulating and make it difficult to wind down.
Buy a New Mattress and a New Pillow
If you’re still struggling with sleep, the problem could be your mattress and pillow and it may be time for an upgrade. Look for a high-quality mattress and supportive pillow for long-lasting comfort and support.
Benefits of Deep Sleep
Deep sleep is the deepest stage of NREM sleep (non-rapid eye movement) —brain activity slows down and muscles relax during deep sleep. During deep sleep, the stress hormone cortisol decreases. Deep sleep also boosts the immune system Verified Source National Library of Medicine (NIH) World’s largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible. View source by producing proteins called cytokines, which fight off infections and diseases.
If you don’t experience deep sleep consistently, you have a higher risk of developing health conditions, including heart disease and Alzheimer’s.
Researchers did a sleep study Verified Source National Library of Medicine (NIH) World’s largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible. View source with mice to see the effects of poor sleep in the arteries. Mice with a normal sleep schedule had less plaque build-up, but sleep-deprived mice showed a significant amount of plaque, leading to high blood pressure and putting the mice at higher risk of heart disease.
Prioritizing sleep may keep you in good health, as we found when we examined correlations between sleep and disease.
The Effects of Sleep Deprivation
Going without adequate sleep can have detrimental effects on nearly every aspect of health and wellbeing. Sleep deprivation disrupts normal functioning, impairs cognitive performance, and increases risk for chronic diseases.
Not getting the recommended 7-9 hours of sleep per night can negatively impact concentration, memory, judgment, and reaction time. Sleep deprivation reduces cognitive abilities and motor coordination, which can lead to poor work and academic performance. Tasks become more challenging when the brain is foggy from lack of sleep.
Sleep also plays a key role in memory consolidation and learning. During deep sleep stages, the brain consolidates memories from the day. Without sufficient sleep, these memory processes are disrupted. New information and experiences cannot be properly stored.
Furthermore, a lack of sleep puts the body under stress, triggering an inflammatory response and the release of hormones like cortisol. Chronic inflammation and stress hormone imbalances are linked to negative health outcomes. High cortisol can suppress the immune system, making it harder to fight infections.
Regularly missing out on deep sleep may also contribute to weight gain and obesity. Appetite hormones become imbalanced due to sleep loss. People who are sleep deprived tend to eat more calories, experience greater hunger cravings, and have an increased preference for high-fat, high-carbohydrate foods.
In the long run, poor sleep habits significantly raise risks for chronic conditions like hypertension, heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. Prioritizing sufficient high-quality sleep is essential for cognitive health, restorative physical processes, balanced hormones and metabolism, and overall well-being.

FAQs
What causes a lack of deep sleep?
A major cause of sleep deprivation is stress. Verified Source National Library of Medicine (NIH) World’s largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible. View source Stress increases cortisol levels in the body and leads to high blood pressure, tension, and alertness. The best way to combat stress is to promote mental well-being around the clock, including having time to relax, being mindful, taking care of our physical health, and tending our social relationships. In the late evenings, it can be helpful to establish a bedtime routine, shut off electronic devices, and enjoy stress-relieving activities, like writing in your journal or taking a warm shower.
How long can you go without sleep?
Staying awake for long periods of time affects your ability to concentrate and focus. Going 24 hours without sleep results in daytime sleepiness, impaired judgment, and poor decision making, and even a weakened immune system. In deep sleep the body releases cytokines, proteins that control the growth and activity of immune system cells to fight off inflammation and infection.
What happens if you don’t get enough deep sleep?
If you’re sleep-deprived, that means you’re spending less time in deep sleep, which disrupts the brain’s ability to store memories. You may struggle to remember what was said during a meeting or have a hard time concentrating on your daily activities. Plus, sleep deprivation affects motor skills, so you may not perform at your best as an athlete if you don’t get enough sleep.
Is it better to get 2 hours of sleep or none?
It’s better to get 2 hours of sleep than none at all. Those two hours, however small, recharge your brain and body enough to make it through the day. Don’t make it a habit, but if you were up all night and have a couple of hours to spare before getting ready for the day, use that time to sleep.
Remember, adults need 7 to 9 hours of sleep. Verified Source Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) The United States’ health protection agency that defends against dangers to health and safety. View source
What happens if you can’t fall asleep?
If you can’t fall asleep, no matter how tired you are, you may have insomnia. Insomnia is one of the most common sleep disorders—about one in seven adults in the United States suffers from insomnia. If you suspect you have insomnia, talk with your doctor or sleep specialist. They can help you find solutions.
Conclusion
Deep sleep enables the growth and repair of muscle tissue and regenerates cells. When you don’t get enough deep sleep, you may wake up feeling sore and may struggle to concentrate. Taking steps like winding down before bedtime and turning off electronic devices an hour before bed can induce sleep by relaxing the body and mind. Following these sleep tips may help you to get the deep sleep you need so you feel at your best.
About the author
Mitchell Tollsen is a graduate student and a freelance writer who’s contributed to the Early Bird blog for three years. Mitchell’s always been fascinated by the science of sleep and the restorative processes our bodies undergo when at rest. The self-titled “Sleep Expert” is always looking for ways to improve his shut-eye, and throughout the years has implemented numerous lifestyle changes and tried dozens of sleep-promoting gadgets to determine the best ways to truly get better rest.
View all posts